There are various types of upper respiratory infections (URIs). Use this guide to understand URIs, associated illnesses, treatment options, and proper care until professional medical attention is available.
Defining Upper Respiratory Infections
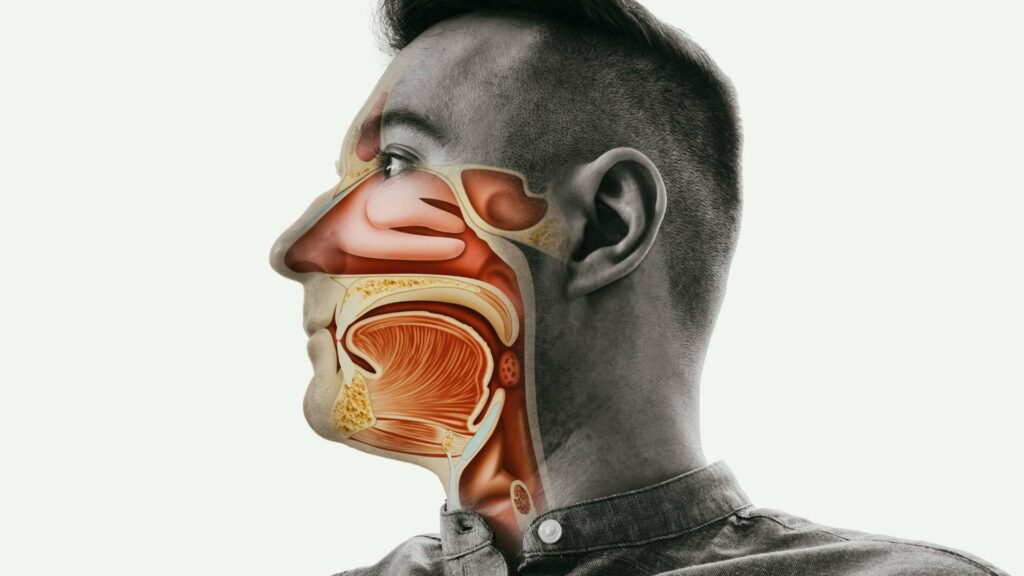
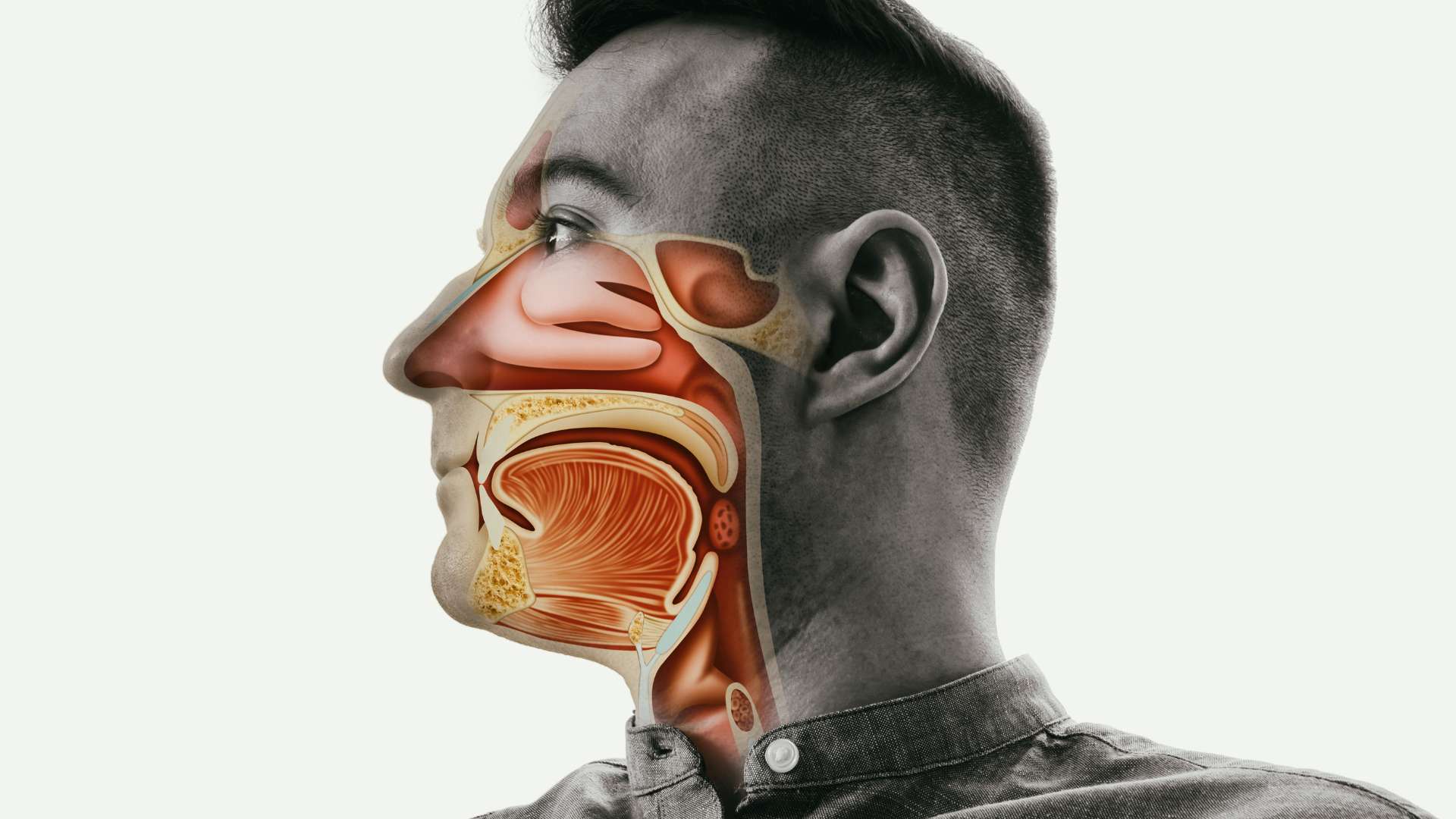
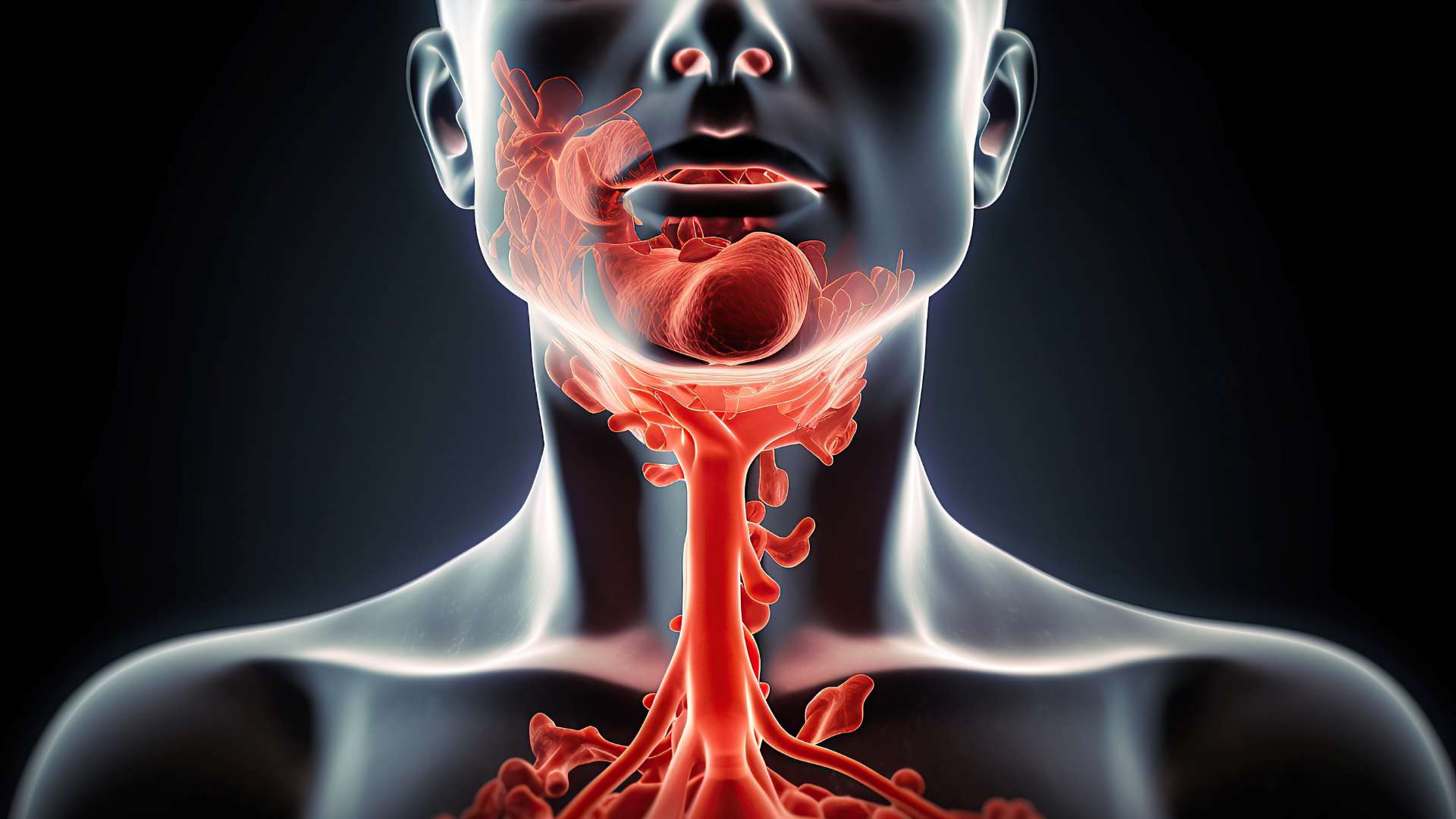
An Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) is a common medical condition that affects the respiratory system, primarily the nose, throat, and sinuses. Viruses often cause URIs, leading to various symptoms, from mild discomfort to more severe respiratory issues.
Types of Upper Respiratory Infections
Common types of URIs include:
Common Cold:
A viral infection affecting the nose and throat, causing symptoms like a runny or stuffy nose, sore throat, cough, and mild fever.
Sinusitis:
Inflammation of the sinus passages, leading to symptoms such as facial pain, pressure, and nasal congestion.
Pharyngitis:
Also known as a sore throat, it causes pain, irritation, and difficulty swallowing due to inflammation of the throat.
Illnesses Caused by Upper Respiratory Infections
URIs can lead to several other illnesses, such as:
Bronchitis:
Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, causing cough, chest discomfort, and mucus production.
Ear Infections:
URIs can cause blockage of the Eustachian tube, leading to ear infections and discomfort.
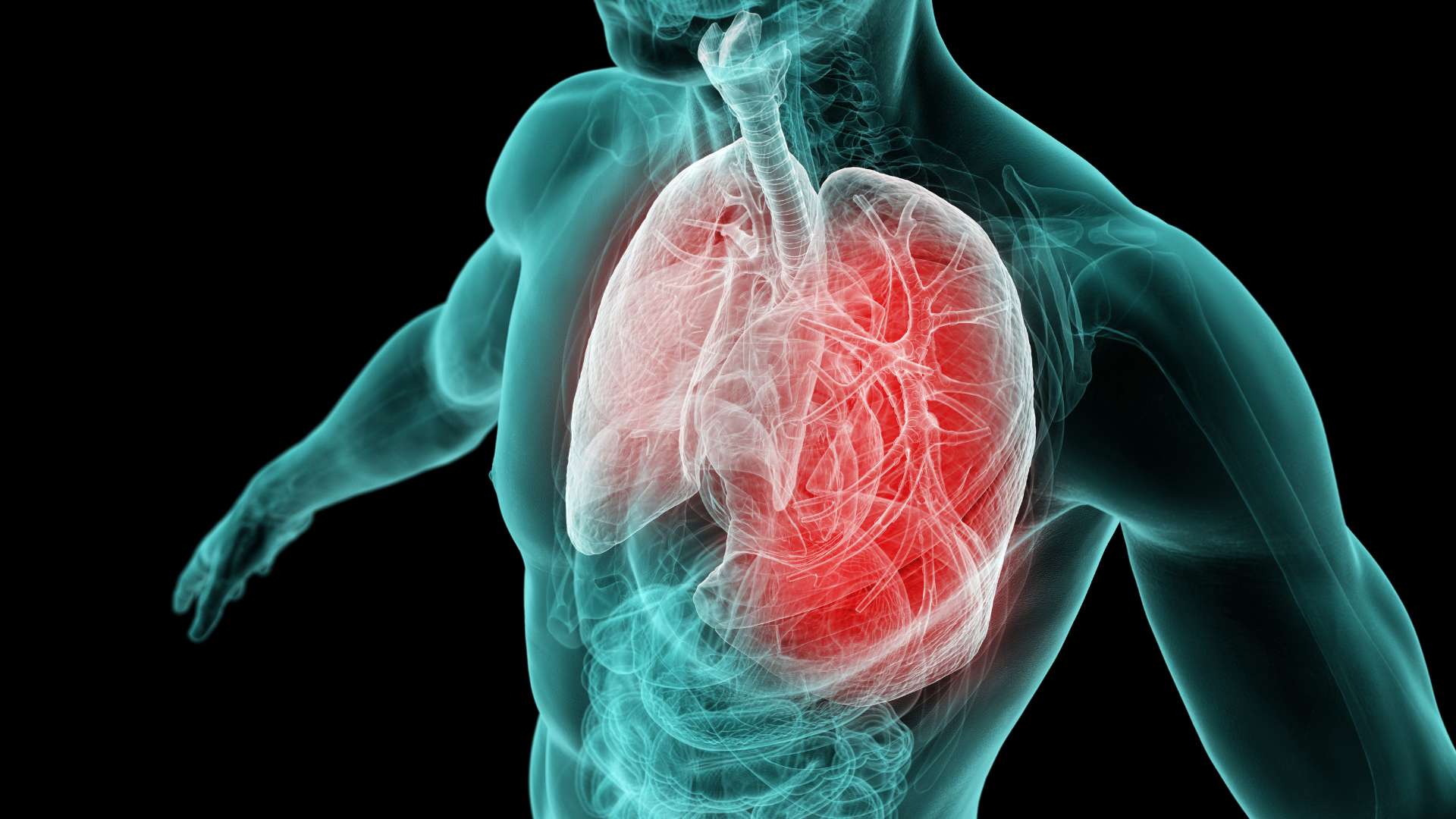
Pneumonia:
In severe cases, a URI can progress to pneumonia, which is characterized by lung inflammation and difficulty breathing.
Treatment for Upper Respiratory Infections
Most URIs are viral in nature, and treatment primarily focuses on managing symptoms and supporting the body’s immune response. This includes:
Rest: Allow the body to recover by getting plenty of rest and avoiding strenuous activities.
Hydration: Drink fluids to prevent dehydration and soothe the throat.
Over-the-Counter Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, decongestants, and cough syrups may help alleviate symptoms.
Self-Care for Upper Respiratory Infections
To care for an upper respiratory infection until medical attention is available, consider the following:
Stay Home: If experiencing symptoms of a URI, it is advisable to stay home to prevent spreading the infection to others.
Hygiene Practices: Practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, to reduce the risk of transmission.
Warm Compresses: Apply warm compresses to soothe sinus pain and pressure.
Frequently Asked Questions About Upper Respiratory Infections
1. Can antibiotics treat URIs?
Antibiotics are ineffective against viral infections, including most URIs. They are prescribed only for bacterial infections or complications arising from a URI.
2. How long does it take to recover from a URI?
Recovery time can vary based on the type of URI and individual health. Most people experience relief from symptoms within a week.
3. Can URIs be prevented?
Practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of contracting a URI.
Contact Occupational Health Services today to request an appointment and learn more about how to protect your employees from URIs and other respiratory conditions. Our experienced medical professionals are here to support your workforce’s health needs and create a healthier work environment for your business.