Occupational Health Services offers valuable insights into sinus infections, addressing their causes, symptoms, and preventive measures. Our comprehensive guide aims to promote a healthy workforce by providing information on sinus infection prevention and management.
What is a Sinus Infection?
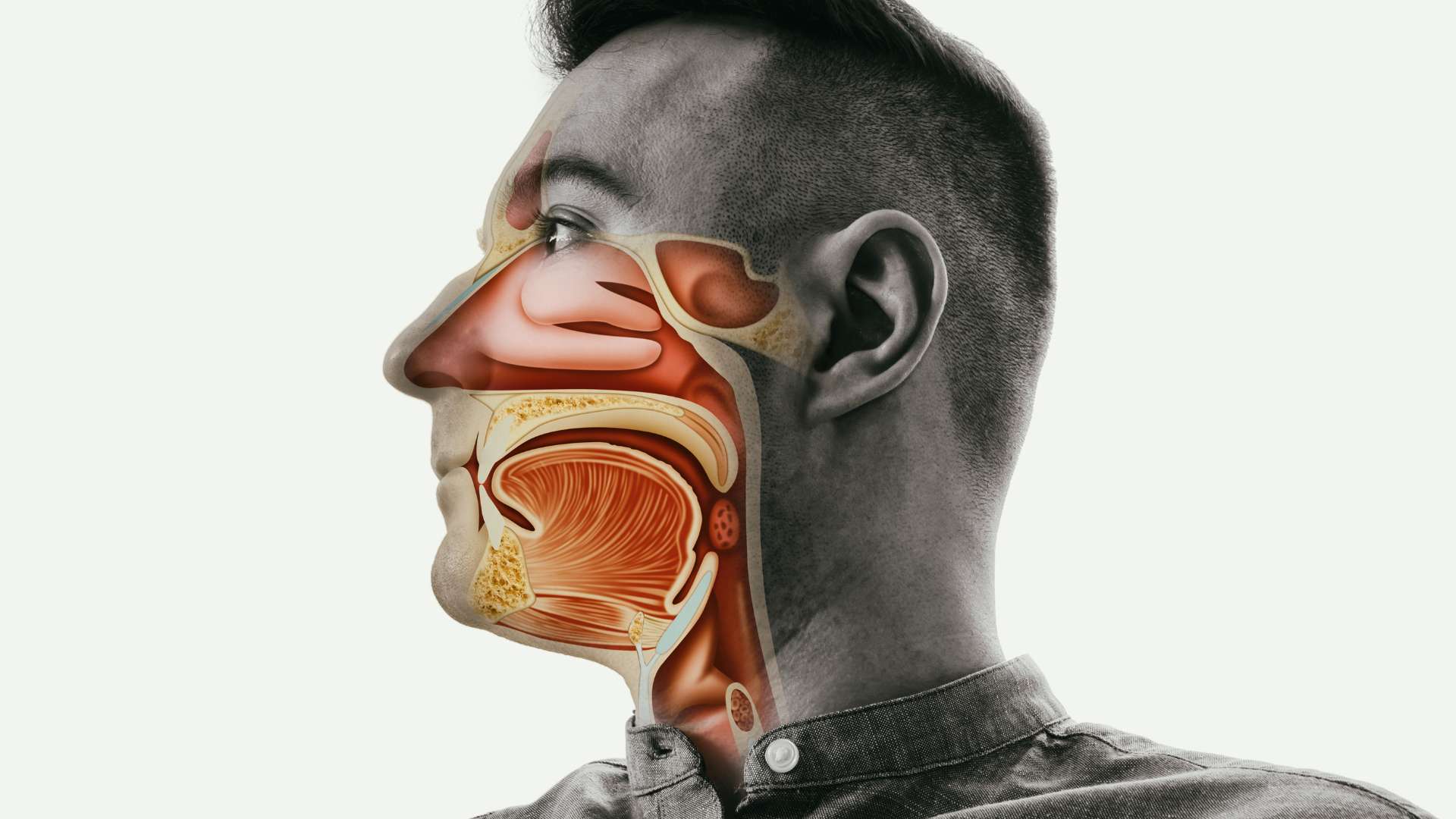
A sinus infection, also known as sinusitis, is an inflammation of the sinuses – the air-filled cavities around the nose and eyes. When the sinuses become blocked and filled with mucus, it creates an environment for bacteria or viruses to grow, leading to a sinus infection.
Causes of Sinus Infections
Sinus infections can be caused by various factors, including:
Viral Infections: The common cold or flu can cause inflammation and lead to a sinus infection.
Bacterial Infections: Bacteria can infect the sinuses, resulting in acute or chronic sinusitis.
Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause swelling and congestion in the sinuses, increasing the risk of infection.
Symptoms of a Sinus Infection
Common symptoms of a sinus infection include:
- Nasal congestion and difficulty breathing through the nose
- Thick yellow or green nasal discharge
- Facial pain or pressure, especially around the eyes, nose, and cheeks
- Headache and tenderness in the forehead or temples
- Cough, fatigue, and a reduced sense of taste or smell
Other Illnesses or Ailments Sinus Infections can Produce
Untreated or recurrent sinus infections can lead to complications such as:
Chronic Sinusitis: Persistent inflammation of the sinuses lasting more than 12 weeks.
Ear Infections: Sinus infections can lead to the spread of infection to the ears.
Asthma Exacerbation: Sinusitis can worsen asthma symptoms in individuals with asthma.
Contracting Sinus Infections in Occupational Fields
Workers in various occupational fields can contract sinus infections due to factors like:
Exposure to Irritants: Occupational exposure to pollutants, allergens, and dust can trigger sinus inflammation.
Close Working Environments: Sharing enclosed spaces with infected individuals increases the risk of transmission.
High-Stress Workplaces: Stress can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
Alleviating Sinus Infection Symptoms and Discomfort
If someone suspects they have a sinus infection, they can take the following steps to alleviate symptoms until they can see a medical professional:
Stay Hydrated: Drinking fluids can help thin mucus and promote drainage.
Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the face can relieve facial pain and pressure.
Nasal Irrigation: Using saline to rinse the nasal passages can reduce congestion.
Preventing Sinus Infections through Training and Education
Proper training and education play a pivotal role in preventing sinus infections in the workplace. Occupational Health Services can inform employees about good hygiene, maintaining clean working environments, and identifying potential sinusitis triggers.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sinus Infections
1. Are sinus infections contagious?
Most sinus infections are not contagious, but the viruses or bacteria that cause them can spread from person to person.
2. When should I seek medical attention for a sinus infection?
Medical attention is recommended if sinus infection symptoms persist or worsen after ten days or if there is severe facial pain or high fever.
3. Can sinus infections be prevented with vaccines?
No specific vaccines target sinus infections, but general vaccinations for the flu and other respiratory illnesses can reduce the risk of diseases.
Occupational Health Services is committed to fostering a thriving and efficient workforce. Contact us now to schedule an appointment and discover how our all-encompassing healthcare services and resources can enhance your employees’ well-being.