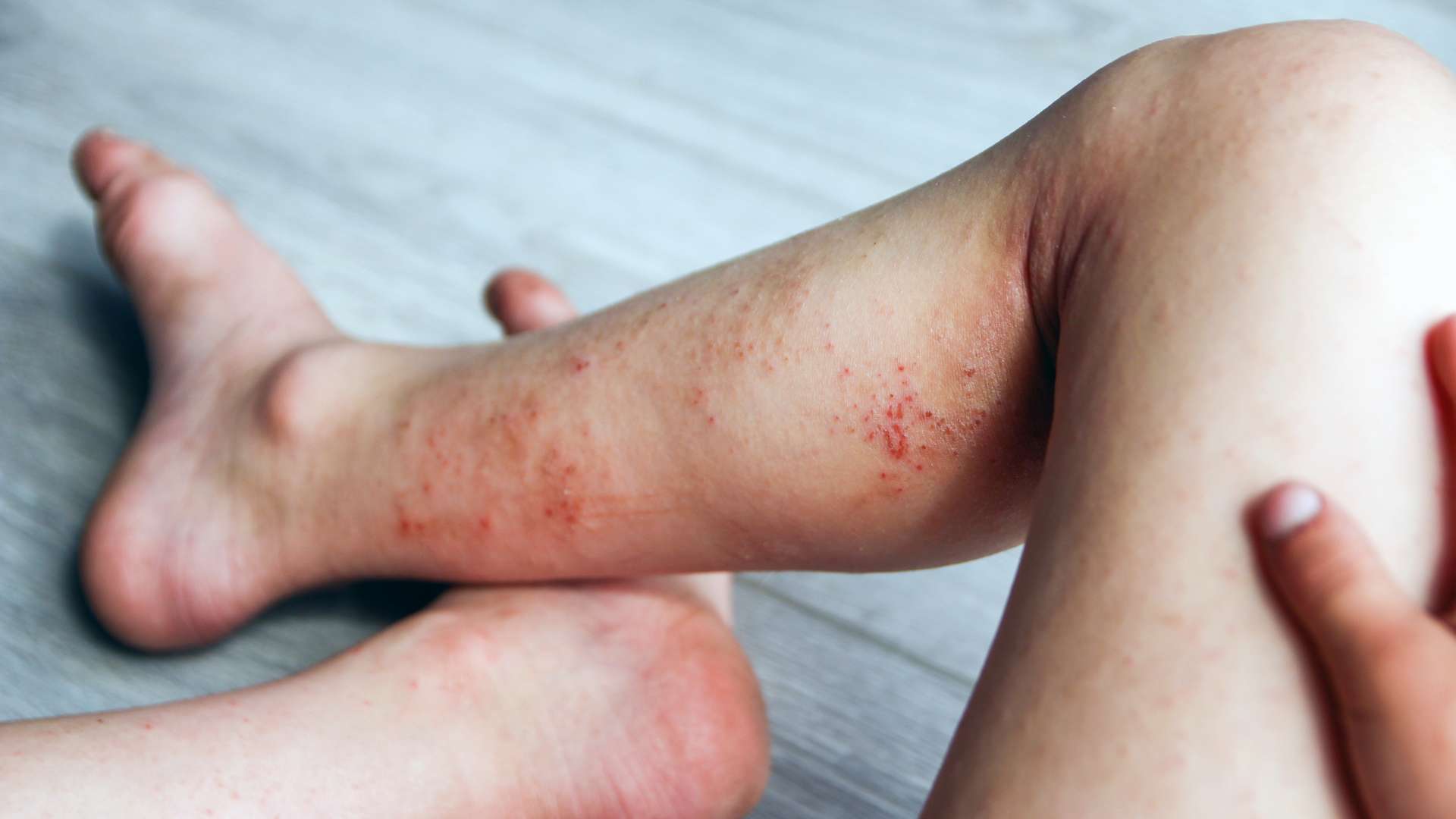
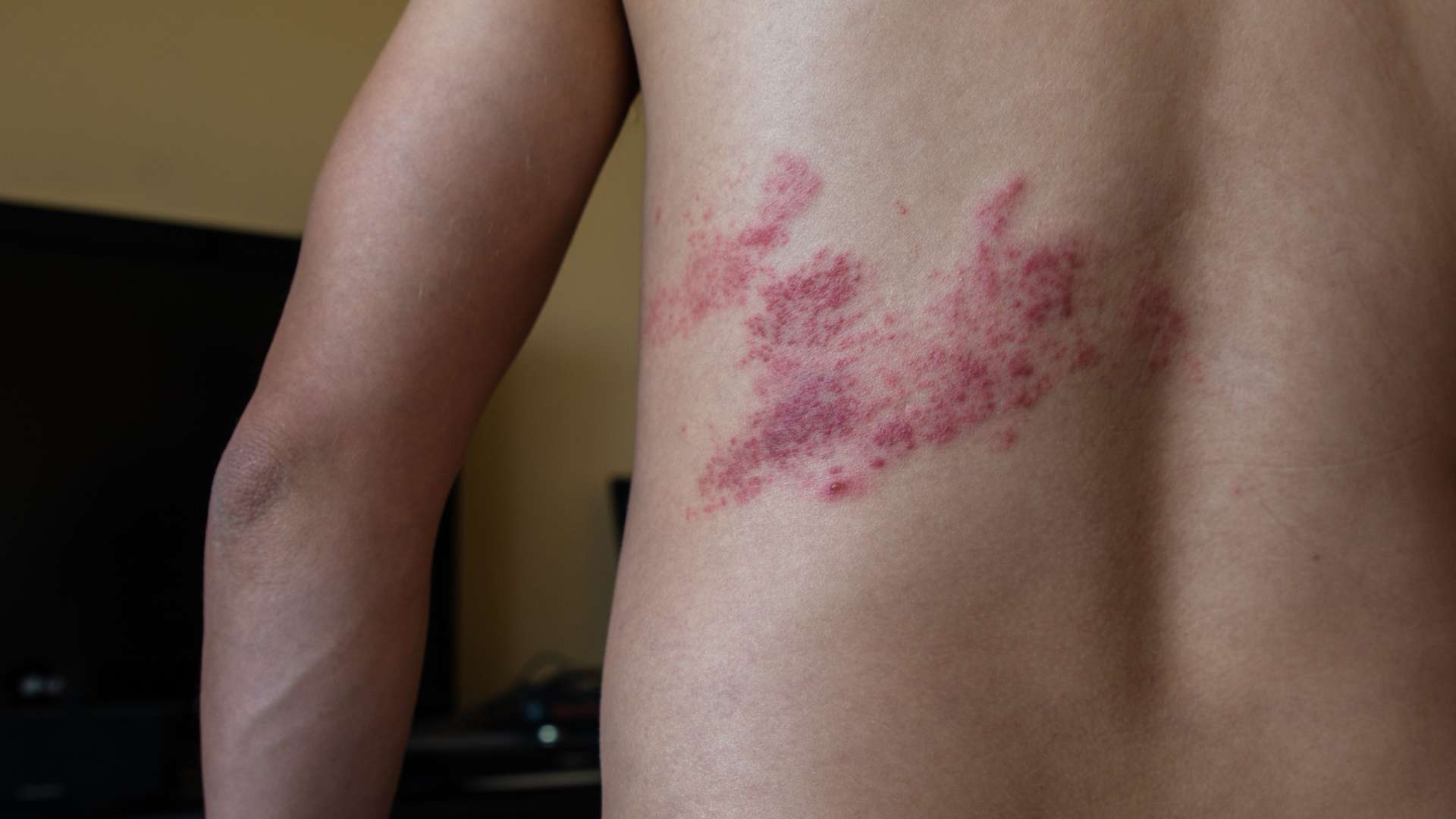
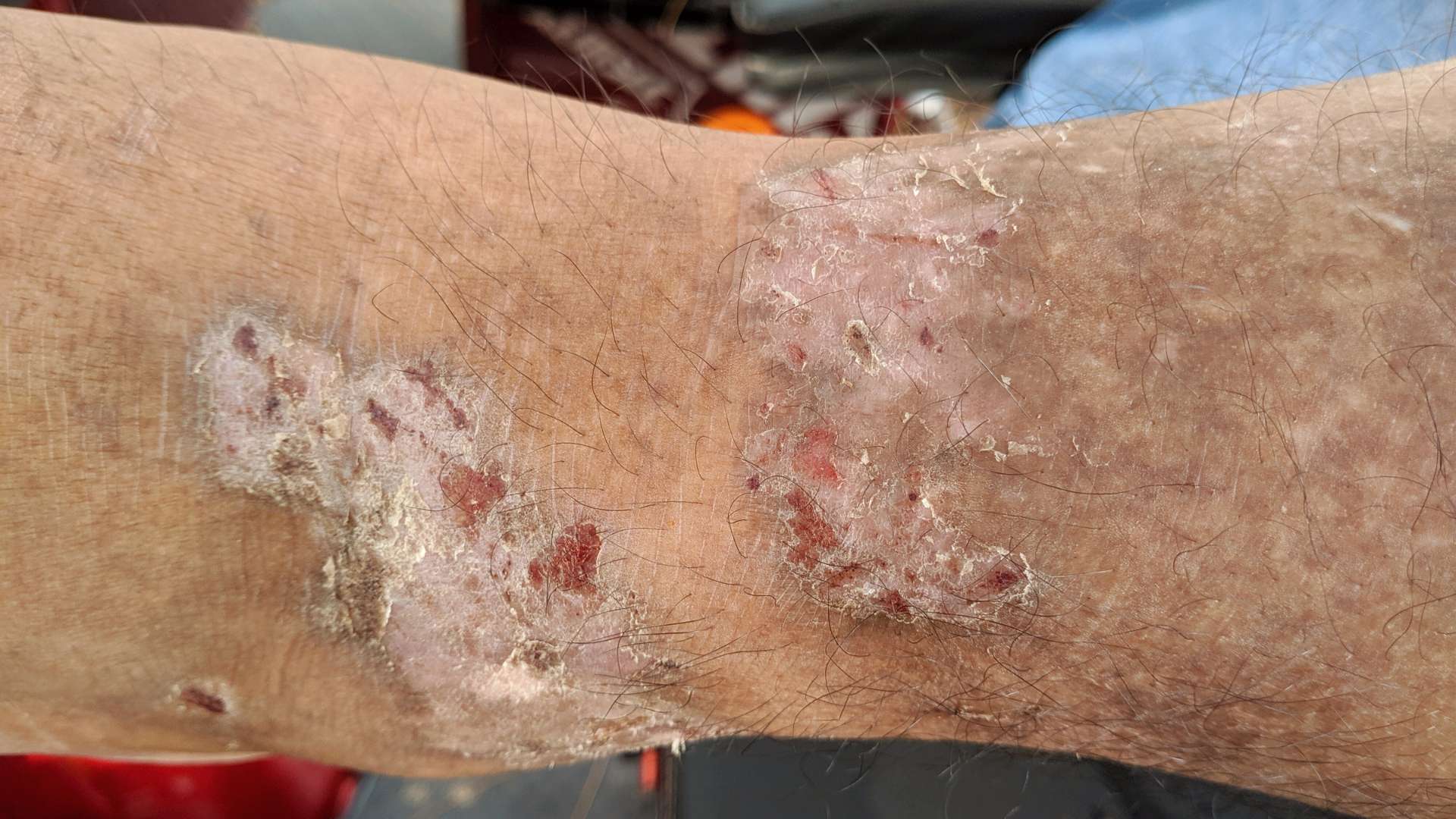
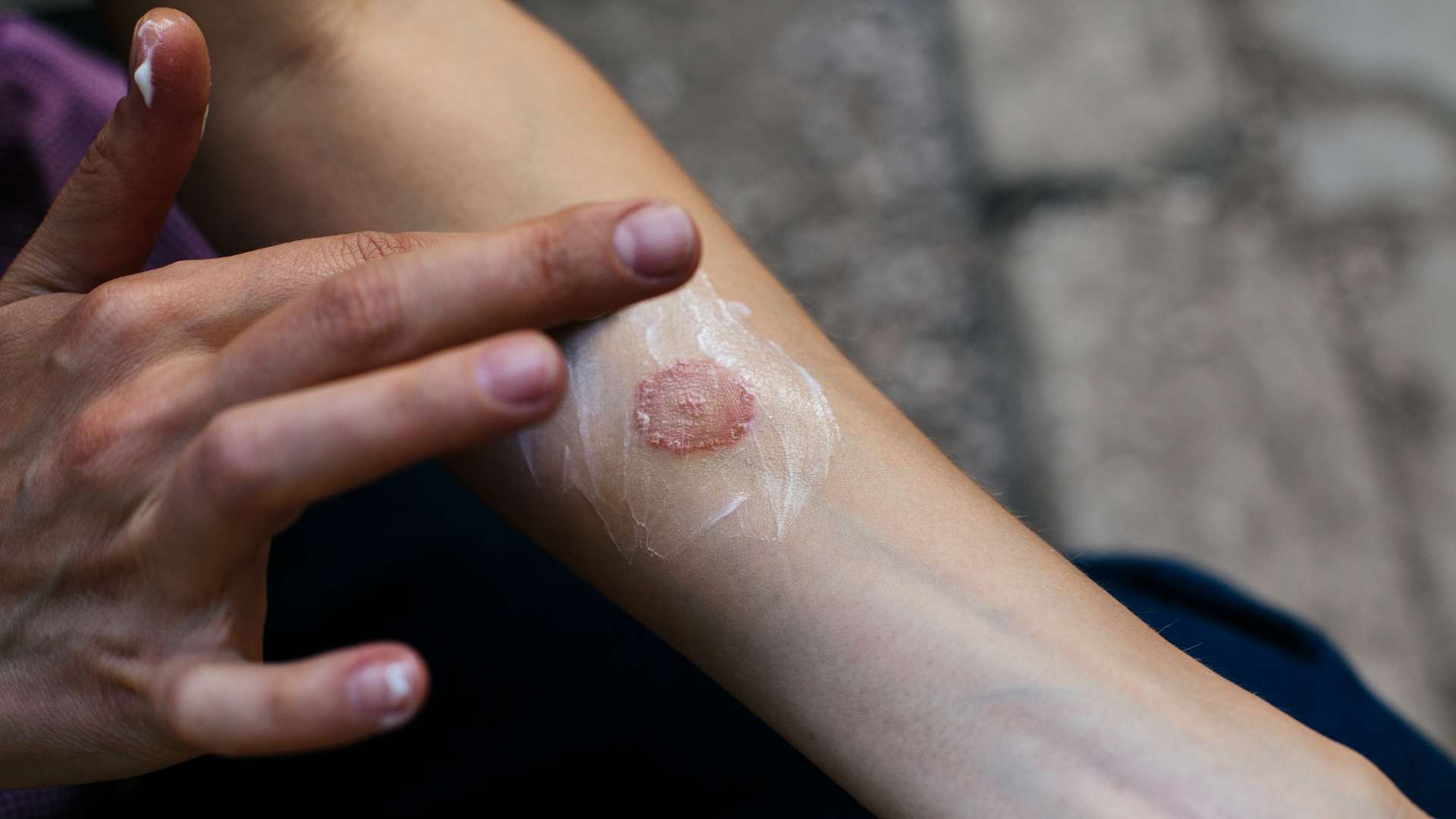
Infectious diseases are illnesses caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, that can be transmitted from one person to another. These diseases can vary in severity, from mild to life-threatening, and can spread through various means, including direct contact, airborne particles, contaminated surfaces, and more.
Occupational Environments
Healthcare Settings: Healthcare workers are at an increased risk of exposure to infectious diseases due to close contact with patients. Diseases like influenza, tuberculosis, and COVID-19 can spread in healthcare facilities without proper precautions.
Travel and Hospitality: Employees in the travel and hospitality industry, such as flight attendants, hotel staff, and restaurant workers, may encounter travelers from various regions and backgrounds, increasing the risk of exposure to infectious diseases.
Laboratory and Research Facilities: Workers in laboratories and research facilities handle infectious agents and biological materials, necessitating strict safety protocols to prevent accidents and exposures.
Substances and Tasks Leading to Infection
Biohazardous Materials: Handling biohazardous materials, including blood, bodily fluids, and contaminated waste, poses a significant risk. Needlestick injuries and improper disposal can lead to the transmission of diseases like HIV and hepatitis.
Close Contact: Jobs that require close physical contact with others, such as massage therapists or personal care aides, may expose employees to contagious conditions like skin infections or respiratory illnesses.
Travel and Commuting: Employees who travel frequently or use public transportation may face a higher risk of contracting infectious diseases due to crowded and enclosed spaces.
Prevention & Training
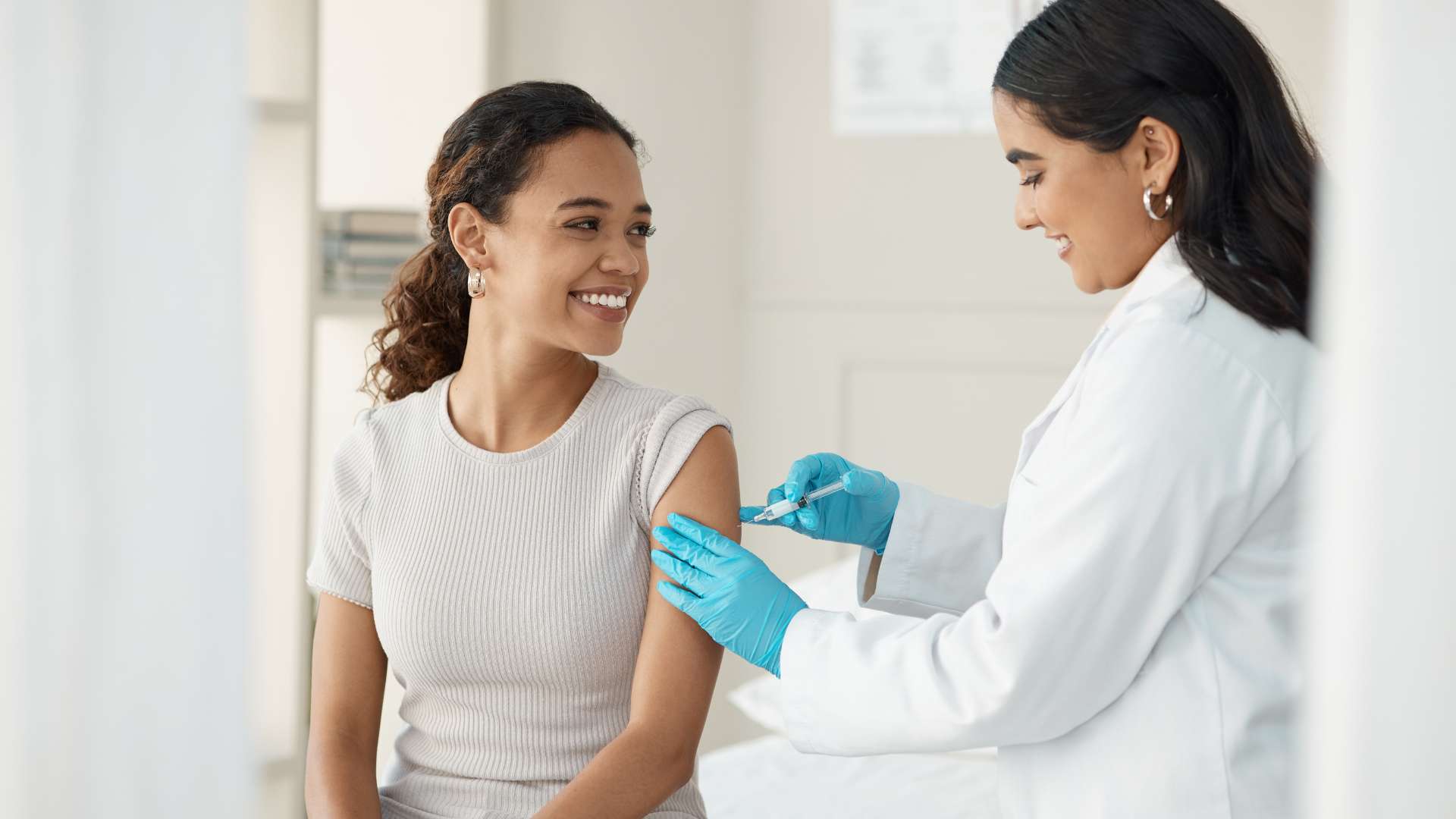
Proper training is essential to prevent the spread of infectious diseases in the workplace. Training programs can educate employees on hygiene practices, personal protective equipment (PPE), proper handwashing techniques, and the importance of vaccination. Workers can also learn how to recognize the signs of infectious diseases and how to respond in case of exposure.
By investing in comprehensive training, employers protect their employees and reduce the risk of outbreaks that can disrupt business operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are common infectious diseases in the workplace?
Common infectious diseases in the workplace include the flu, COVID-19, tuberculosis, hepatitis, MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), and norovirus.
How can employers reduce diseases in the workplace?
Employers can reduce the risk by implementing infection control measures, providing PPE, conducting health screenings, offering vaccination programs, and providing comprehensive employee training on infection prevention.
How can Occupational Health Services help businesses?
Occupational Health Services offers tailored solutions, including infection control assessments, employee training programs, vaccination clinics, and outbreak management support to protect your workforce and prevent disease transmission.
Choose Occupational Health Services for a Healthier Workplace
At Occupational Health Services, we prioritize the health and safety of your workforce. Our experienced team provides a range of services and resources designed to reduce the spread of infectious diseases, including infection control assessments, employee training, and vaccination programs.
Learn more about our services and resources, then contact us today to request an appointment. Together, we can create a workplace where infectious diseases are effectively managed, and your employees can enjoy a safer and healthier work environment. Your workforce’s health is our priority.